
This article is a brief guide to the most popular types of hydraulic fittings and connections. It is essential that you correctly identify fittings so that you can connect the right systems.
These measurements are for fitting identification using the table at the end of the page.
You will need:
- Callipers
- Thread pitch gauge
- Seat angle gauge
Step 1.
Is the fitting female or male?
- Female—the threads are on the inside of the nut and measured by the inside diameter (ID)
- Male—the threads are on the outside of the nut and measured by outside diameter (OD)

Step 2.
Is the fitting tapered or straight? If you cannot see this use callipers to measure the beginning and end of the fitting. A parallel thread will have a method of sealing, whereas taper threads seal by thread contact between the male and female ports.
- Tapered—the diameter get smaller towards the end of the female fitting or gets larger towards the end of a male fitting.
- Straight (parallel)—the threads are the same diameter end to end.

Step 3.
Determine the thread size using callipers measure the OD of the male thread or the ID of the female thread. Beware of worn threads when checking the table for an exact match.

Determine thread angle using a seat angle gauge. Match the centreline of the seat gauge with the axis of the coupling.
Step 4.
Determine thread pitch – threads per inch.
Use a thread pitch gauge to measure the threads per inch. If you do not have a thread pitch gauge, count the number of thread crests over ¼” length and multiply it by 4. For example, if there are 3.5 thread crests, multiply by 4 to get 14—the number of threads per inch. You can also use a pitch gauge against a lighted background. Measure several threads to ensure that you have the right number.
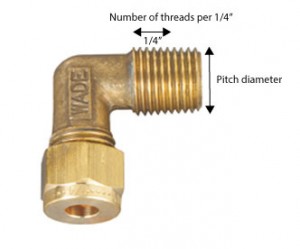
Step 5.
Check the results against the charts below.
Male Parallel Fitting Dimensions
| Thread | Threads per inch | Pitch | Outside diameter mm | Inner diameter mm |
| 1/16 | 28 | 0.907 | 7.723 | |
| 1/8 | 28 | 0.907 | 9.728 | 8.566 |
| 1/4 | 19 | 1.337 | 13.157 | 11.445 |
| 3/8 | 19 | 1.337 | 16.662 | 14.95 |
| 1/2 | 14 | 1.814 | 20.995 | 18.631 |
| 5/8 | 14 | 1.814 | 22.991 | 20.587 |
| 3/4 | 14 | 1.814 | 26.441 | 24.117 |
| 1 | 11 | 2.309 | 33.249 | 30.291 |
| 1 1/4 | 11 | 2.309 | 41.910 | 34.939 |
| 1 1/2 | 11 | 2.309 | 47.803 | 44.845 |
| 2 | 11 | 2.309 | 59.614 | 56.656 |
| 2 1/2 | 11 | 2.309 | 75.184 | 72.226 |
| 3 | 11 | 2.309 | 87.884 | 84.926 |
| 4 | 11 | 2.309 | 113.030 | |
| 5 | 11 | 2.309 | 138.430 |
Male Tapered Fitting Dimensions
| Thread | Thread per inch | Pitch | Outside diameter mm | Inner diameter mm |
| 1/16 | 28 | 0.907 | 7.723 | 6.561 |
| 1/8 | 28 | 0.907 | 9.728 | 8.566 |
| 1/4 | 19 | 1.337 | 13.157 | 11.445 |
| 3/8 | 14 | 1.337 | 16.662 | 14.95 |
| 1/2 | 11 | 1.814 | 20.995 | 18.631 |
| 3/4 | 11 | 1.814 | 26.441 | 24.117 |
| 1 | 11 | 2.309 | 33.249 | 30.291 |
| 1 1/4 | 11 | 2.309 | 41.91 | 38.952 |
| 1 1/2 | 11 | 2.309 | 47.803 | 44.845 |
| 2 | 11 | 2.309 | 59.614 | 56.656 |
| 2 1/2 | 11 | 2.309 | 75.184 | 72.226 |
| 3 | 11 | 2.309 | 87.884 | 84.926 |
| 4 | 11 | 2.309 | 113.03 | 110.072 |
| 5 | 11 | 2.309 | 138.43 | 135.472 |
BFPA Training – Indanc Academy
Industrial Ancillaries Academy runs a number of courses in partnership with the BFPA specifically designed for anyone who works with hydraulics.
Foundation Safety Course
Basic hydraulics health and safety course.
Hose Assembly Skills Course
2 day course on hose assembly procedure, including routing and installation.
Hose Integrity, Inspection and Management Course
Health and safety assessment training including risk analysis and competence.
Small Bore Tubing Integrity Course
Safety training in the manufacture of small bore tubing assemblies.
Call us on 01246 242050 or get in touch via our Contacts page to find out more details about our courses and course dates.
Other related articles
Hydraulic Hose Safety Issues
Find out how important safety is for the hydraulic hose industry. Particularly, how and why the majority of accidents happen and how to prevent them.
What is the difference between pipes and tubes?
Do you know what the difference is and does it matter? The answer is ‘yes’ especially if you work in engineering or construction. Find out why it matters and when you would use tube or pipe by reading this article.
What is the difference between NPT and BSP fittings?
There are a number of different sizing standards used throughout the world. But, do you know which one you should use and what the difference is between them. No. Then read this article and find out.
What is the difference between hydraulics and pneumatics?
They both convert fluid pressure to mechanical motion. The major difference, however, is that one works with air and the other with liquids. Find out which is which and more with this article.
The principles of pipe and tube bending
What happens to metal when you bend it? If you want to find out, then read this article about tube bending processes and problems.
A quick guide to the life of a hose from purchasing, installing, operating and replacement.
