Pipe and Tube
What’s the Difference?
 The words ‘pipe’ and ‘tube’ are often used interchangeably to mean a cylinder used to transport liquid or gas. This definition does not matter much unless you are referring to tube or pipe used in industry, especially engineering, in which case there are fundamental differences between the two. These differences are outlined below.
The words ‘pipe’ and ‘tube’ are often used interchangeably to mean a cylinder used to transport liquid or gas. This definition does not matter much unless you are referring to tube or pipe used in industry, especially engineering, in which case there are fundamental differences between the two. These differences are outlined below.
Uses
Tube is primarily used for structural purposes such as scaffolding.
Pipe is used to transport liquids or gases.
Sizing
Tube and pipe are measured differently when determining the required size.
One thing they do have in common is that for both pipe and tube there are three important dimensions:
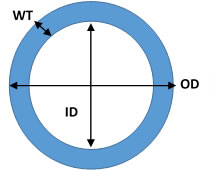
- Outside diameter (OD)
- Inside diameter (ID)
- Wall thickness (WT)
They are related by the following equation:
OD = ID + 2 * WT
Tube is measured by the exact outside diameter (OD) with a set range of wall thickness. The wall thickness is important as the strength of the tube depends on this.
Pipe is measured by a nominal OD. The most important property is the capacity or inside dimension (ID).
NPS (Nominal Pipe Size) is a US standard measured in inches used to designate pipe diameter and thickness. DN (diamètre nominal/nominal diameter/Durchmesser nach Norm), in which sizes are measured in millimetres, is the European and international equivalent.
 Structure
Structure
Tube does not have to be round it can be square or rectangular. Tube is usually seam welded. Copper and brass tube can be shaped but other ranges of tube are typically rigid. Because tube has to carry weight, it is usually stronger than pipe.
Pipe, on the other hand, is always round and rigid as it cannot be shaped without special equipment. Pipe is usually seamless and pressure rated because it is used for transporting liquids or gases, so it is important that there is no leakage.
Cost
Because of its structural use, tube tends to be more expensive than pipe as it has higher tolerance levels.
Summary
Tube
- Tube is used for structural purposes
- Tube is measured by OD
- Tube is sized in exact OD (exact outside diameter and set range of wall thickness of tubing) *
- The most important property of tube is the wall thickness (WD)
- Tube is usually more expensive as tolerances higher
- Shape can be square or rectangular not just round
- Tube is typically rigid, with the notable exception of Copper and brass tube which can be shaped
- Tube is seam welded
- Tube is stronger than pipe, as strength depends on wall thickness
*However, when using copper pipe the OD is 1/8th larger than the stated OD. Stainless steel, aluminium, and steel tubing measurements are exact.
Pipe
- The main purpose of pipe is to transport gases or fluids as a vessel, used in pipeline and piping systems
- Pipe is measured by ID
- Pipe is sized in Nominal Pipe Size—nominal outside diameter different from measured OD and schedule (wall thickness) of pipe
- The most important property of pipe is the capacity or ID (inside diameter)
- Pipe is always round in shape
- Pipe is invariably rigid and cannot be shaped without special equipment
- Pipe is usually seamless
- Pipe is pressure rated, depending on what it is designed to carry
BFPA Training at the IA Academy
Industrial Ancillaries Training Academy runs a number of courses in partnership with the BFPA, designed for anyone who works with hydraulics.
Foundation Safety Course
Basic hydraulics health and safety course.
Hose Assembly Skills Course
2-day course on hose assembly procedure, including routing and installation.
Hose Integrity, Inspection and Management Course
Health and safety assessment training including risk analysis and competence.
Call us on 01246 242050 or get in touch through our Contacts page to find out more details about our courses and course dates.
Other related articles
Hydraulic Hose Safety Issues
Find out how important safety is for the hydraulic hose industry. Learn how and why the majority of accidents happen and how to prevent them.
What is the difference between NPT and BSP fittings?
There are a number of different sizing standards used throughout the world. Do you know which one you should use and what the difference is between them. No. Then read this article and find out.
What is the difference between hydraulics and pneumatics?
They both convert fluid pressure to mechanical motion. The major difference is that one works with air and the other with liquids. Find out which is which and more with this article.
The principles of pipe and tube bending
What happens to metal when you bend it? Find out about bending processes and problems from this article.
